
TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)
發(fā)布者:信康 瀏覽次數(shù):
產(chǎn)品名稱:TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)CAS:761437-28-9別名:2-[[5-氯-2-[[2-甲氧基-4-(4-嗎啉基)苯基]氨基]-4-嘧啶基]氨基]-N-甲基苯甲酰胺;2-[[5-氯-2-[[2-甲氧基-4-(4-嗎啉)苯基]氨基]-4-嘧啶]氨基]-N-甲基苯甲酰胺英文名:TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)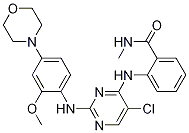 []
[] - 生物活性TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)是一種有效的FAK抑制劑,IC50為5.5 nM����,最有效作用于Pyk2,對(duì)InsR, IGF-1R��, ALK和c-Met作用效果比其弱10到100倍左右���。
- 體外研究NVP-TAE226 (< 1 μM) inhibits extracellular matrix-induced autophosphorylation of FAK (Tyr397) in serum-starved U87 cells. NVP-TAE226 (< 1 μM) also inhibits IGF-I-induced phosphorylation of IGF-1R and activity of its downstream target genes such as MAPK and Akt in both U87 and U251 cells. NVP-TAE226 (<10 μM) retards tumor cell growth and attenuats G(2)-M cell cycle progression associated with a decrease in cyclin B1 and phosphorylated cdc2 (Tyr15) protein expression in both U87 and U251 cells. NVP-TAE226 (1 μM) inhibits tumor cell invasion by at least 50% compared with the control in an in vitro Matrigel invasion assay in glioma cell lines. NVP-TAE226 (1 μM) treatment of glioma cell lines containing wild-type p53 mainly exhibits G(2)-M arrest, whereas glioma cell lines bearing mutant p53 undergoes apoptosis, as evidence by detection of caspase-3/7 activation and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage and by an Annexin V apoptosis assay. NVP-TAE226 (5 μM) inhibits phosphorylation of FAK in the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-AS. NVP-TAE226 (<10 μM) treatment of the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-AS leads to decrease in cellular viability, cell cycle arrest, and an increase in apoptosis. NVP-TAE226 (0.1 μM-10 μM) inhibits tube formation of HMEC1 cells.
- 體內(nèi)研究NVP-TAE226 (75 mg/kg) significantly increases the survival rate of mice bearing intracranial glioma xenografts. NVP-TAE226 (100 mg/kg, oral) exerts significant decrease in microvessel density in a human colon cancer model in SCID mice. NVP-TAE226 (100 mg/kg, oral) efficiently inhibits MIA PaCa-2 human pancreatic tumor growth without body weight loss in vivo model. NVP-TAE226 inhibits 4T1 murine breast tumor growth and metastasis to the lung in a dose-dependent manner in vivo model, associated with inhibition of FAK autophosphorylation at Y397 and Akt phosphorylation at Serine473.
 []
[]